The Earth is No Longer Blue: NASA’s groundbreaking findings about our planet’s changing appearance are causing a stir: Earth is becoming greener. This shift, called the “greening Earth effect,” signals a significant change in how the planet’s ecosystems are evolving, and it’s not just about more trees or lush landscapes. This greening is driven by climate change, human activity, and nature’s response to rising carbon dioxide levels. Let’s break down what’s happening, why it matters, and what it means for our future.
The Earth is No Longer Blue
NASA’s discovery that the Earth is turning greener is both a hopeful sign and a warning bell. While the increase in vegetation suggests that plants are trying to absorb more CO₂, the reality is that our climate crisis is far from over. The greening effect is a temporary fix, and it highlights the need for more serious action on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As we continue to see changes in Earth’s ecosystems, it’s crucial for governments, organizations, and individuals to focus on sustainable solutions—from tree planting and carbon sequestration to reducing fossil fuel consumption. The more we understand these dynamics, the better equipped we’ll be to protect our planet for future generations.
| Key Findings | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Earth’s Vegetation | Satellite data shows 25%-50% of Earth’s vegetated areas have become greener between 1982-2015. |
| Main Driver: CO₂ Fertilization | 70% of greening is due to increased atmospheric CO₂, enhancing plant growth. |
| Human Influence | Countries like China and India are major contributors to global greening via tree planting efforts. |
| Greening and Carbon Sequestration | More vegetation can absorb CO₂, providing a temporary buffer against climate change. |
| Risks of Climate Change | While greening helps, higher CO₂ levels are also accelerating global warming and causing ecosystem disruptions. |
| Official Source | NASA’s Earth Science News |
The Greening Earth Effect: What Is It?
The Earth is no longer blue in the same way we once saw it from space. If you were to look at satellite images from the last few decades, you’d notice that the planet’s surface is getting greener. But why?
This greening effect has been documented by NASA through decades of satellite observations. Between 1982 and 2015, 25% to 50% of Earth’s vegetated areas have seen significant growth. While you might think that this increase in vegetation sounds like a good thing, the truth is more complicated. The changes in Earth’s appearance are both a result of human actions and a response to a rapidly changing climate.
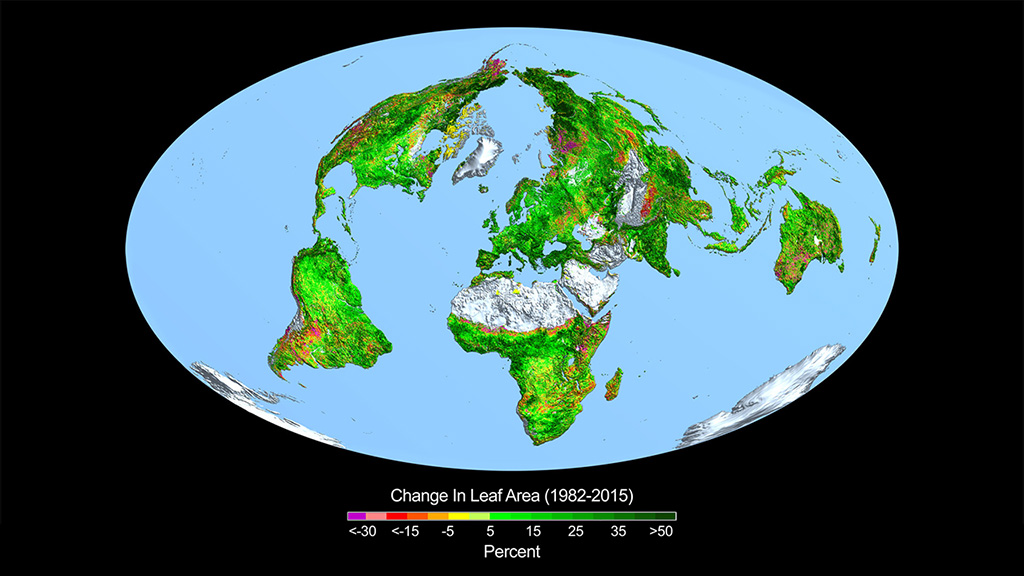
Why The Earth is No Longer Blue?
At first glance, more greenery might seem like a win, right? The increase in plant growth is mainly driven by carbon dioxide (CO₂), a greenhouse gas that plants use during photosynthesis. This process helps plants grow faster and stronger. But here’s the catch: while more CO₂ may boost plant growth, it’s also the primary cause of global warming and climate change.
So, what’s going on? How can CO₂ both help plants grow and warm the planet? Let’s dive into the science of greening and understand the full picture.
Key Drivers of the Greening Effect
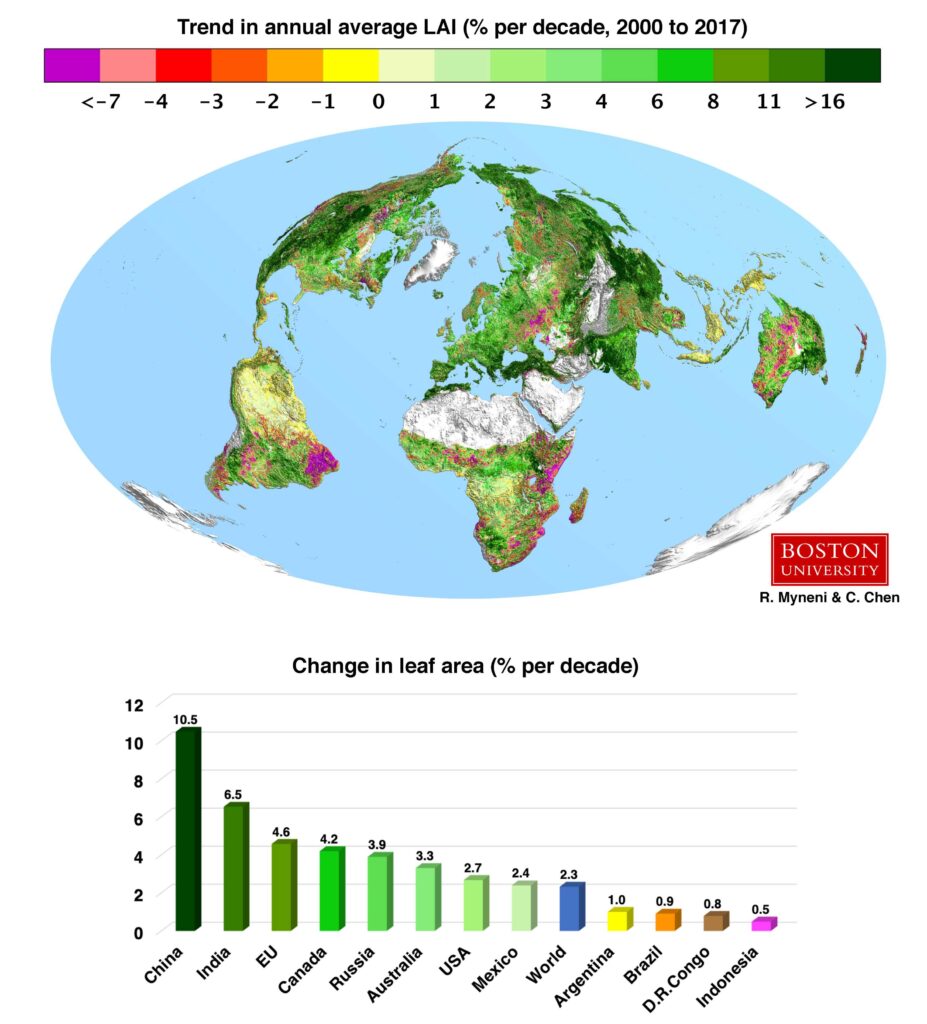
- CO₂ Fertilization: Over 70% of the observed greening is a direct result of increased CO₂ in the atmosphere. This phenomenon, called CO₂ fertilization, is essentially nature’s way of responding to excess carbon. Plants use CO₂ to photosynthesize, so with more CO₂ in the air, plants can grow faster. However, this boost isn’t endless—plants may eventually reach a point where the extra CO₂ no longer has the same effect.
- Nitrogen Availability: An additional 9% of the greening is attributed to increased nitrogen levels. Nitrogen is essential for plant growth, and much of it comes from agricultural activities. As nitrogen levels rise, plants have more of the nutrients they need to grow.
- Human Activity: In places like China and India, large-scale tree planting programs have significantly contributed to the increase in vegetation. These countries have made efforts to green their landscapes, which is helping absorb some of the CO₂ in the atmosphere.
The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: Implications of the Greening Effect
While the greening of Earth may seem like a positive sign, there are both benefits and risks that we must consider. Let’s take a look at what this change really means for our planet.
Benefits of Greening: Carbon Sequestration
One of the benefits of increased vegetation is its ability to sequester carbon. In simple terms, plants absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis and store it. This means that the more plants we have, the more CO₂ can be locked away, temporarily reducing the effects of climate change. However, this is a temporary fix. Over time, plants may become saturated and less effective at absorbing CO₂.
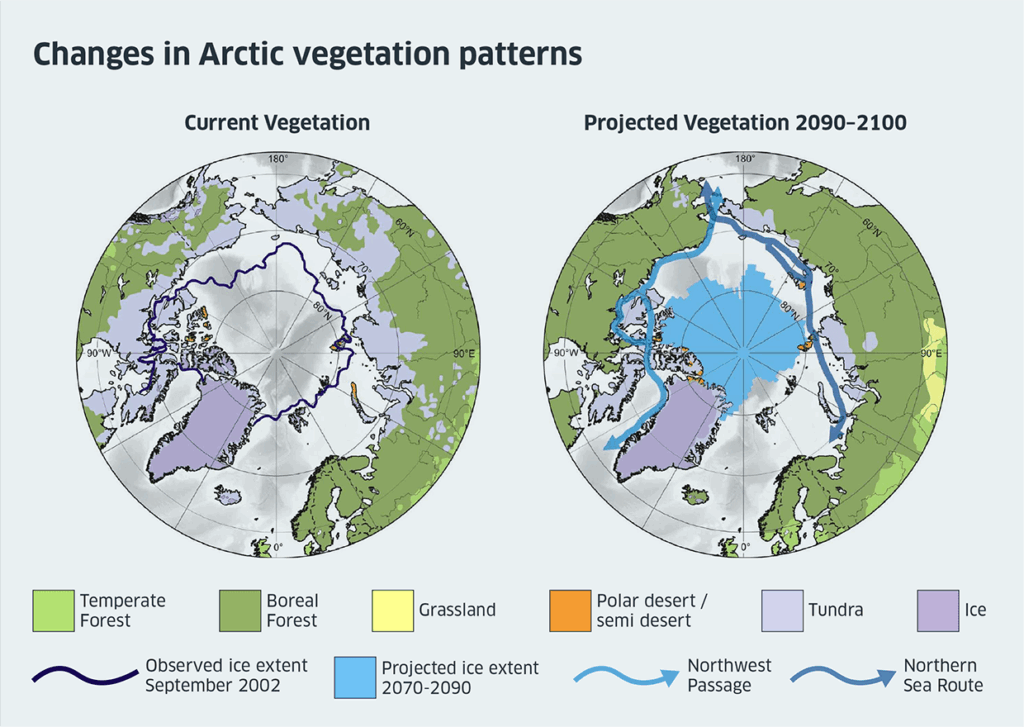
Risks of Over-Greening: Disruption of Ecosystems
In some areas, like the Arctic, the warming climate is enabling plants to move into areas previously dominated by ice and snow. This shift in vegetation can lead to disrupted ecosystems. For instance, in tundra regions, the spread of plants can change the natural habitat of animals that rely on the cold, bare landscape.
Additionally, the rapid rise in vegetation might not be a cure-all for climate change. While plants can absorb CO₂, too much CO₂ can negatively affect plant health and even deplete atmospheric oxygen, as we burn more fossil fuels to produce the CO₂.
Climate Change Acceleration
Despite the greening effect, climate change is still progressing at an alarming rate. Rising temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and melting ice caps are all reminders that we cannot rely solely on plant growth to mitigate the effects of global warming. The real solution lies in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and finding ways to limit the damage already done.
Additional Impacts of the Greening Earth
While the greening effect has been celebrated for its potential to absorb carbon, it has other, less visible impacts that affect not only the environment but also global weather patterns. These changes are subtle but important.
The Impact on Global Rainfall
Research has shown that areas experiencing increased vegetation may influence rainfall patterns. More plants can increase the amount of moisture released into the atmosphere, which could affect regional weather systems. This could mean more rainfall in some regions and potentially droughts in others, disrupting water resources and agricultural cycles.
Vegetation Shifts in Ecosystems
Some ecosystems are not prepared for the change in vegetation types. For example, as temperatures rise, species that once thrived in cold climates may be replaced by plant species better suited for warmer conditions. This may force certain animal species to adapt or relocate, creating a domino effect throughout the food chain.
Practical Solutions: What Can We Do About It?
So, what can we do to keep things in check? The reality is that while Earth’s vegetation is responding to rising CO₂, the true solution to climate change lies beyond this greening trend.
1. Promote Reforestation and Afforestation
Planting more trees is one of the most direct ways to contribute to the greening of Earth. Countries should continue to invest in large-scale tree planting programs. But it’s crucial to ensure that these efforts don’t replace natural ecosystems like rainforests or other critical habitats.
2. Reduce Carbon Emissions
As global citizens, we must prioritize reducing carbon emissions by adopting cleaner energy sources, like wind and solar, reducing waste, and supporting policy changes aimed at combating climate change. Transitioning away from fossil fuels is the most significant step we can take to prevent the harmful effects of increased CO₂.
3. Support Sustainable Agriculture
Agricultural practices must also evolve. By adopting sustainable farming techniques, we can reduce the amount of CO₂ released into the atmosphere and also enhance soil health, which can store more carbon.
4. Invest in Carbon Capture Technology
Carbon capture technology is becoming increasingly important in the fight against climate change. These systems capture CO₂ before it enters the atmosphere, preventing it from exacerbating the warming effect.
The Benefits of Green Living: How Eco-Conscious Homes are Changing the Market
Revealed by NASA: How One Simple Houseplant Can Eliminate Dangerous Toxins from Your Air!
Revolutionary Mexican Invention Transforms Air Into Drinkable Water—How It’s Set to Impact the World