Is 65 or 67 Your Full Retirement Age? When it comes to Social Security benefits, understanding your Full Retirement Age (FRA) is crucial. The FRA is the age at which you’re eligible to receive the full Social Security benefits you’ve earned through years of work. For decades, many people considered 65 the magic age to retire and start collecting Social Security. However, as life expectancy increases and the Social Security system faces financial challenges, the full retirement age has risen, and for those born in 1960 or later, it’s now 67. Let’s dive into what this means for you, how it affects your benefits, and what strategies you can consider for a better retirement plan.
Is 65 or 67 Your Full Retirement Age?
Understanding Full Retirement Age (FRA) is one of the most important steps in planning your Social Security retirement benefits. For those born in 1960 or later, your FRA will be 67, which means you’ll need to wait until this age to receive 100% of your benefits. Whether you choose to claim earlier or delay for higher monthly payments, it’s important to consider your personal health, finances, and life expectancy when making this decision. If you’re unsure about when to start taking benefits, consult a financial advisor to explore all your options and create a strategy that aligns with your long-term goals.

| Key Detail | Information |
|---|---|
| Full Retirement Age (FRA) for 1960+ Births | 67 years old |
| FRA for Those Born 1943–1954 | 66 years old |
| FRA for Those Born 1955–1959 | Between 66 years, 2 months and 66 years, 10 months |
| Early Retirement Option | Available at age 62 (with a permanent reduction in benefits) |
| Delayed Retirement | Increases benefits by 8% per year if delayed until age 70 |
| Social Security Website | SSA.gov |
| 2025 FRA Impact | Affects those born in 1960 and later, who now must wait until age 67 |
What is Full Retirement Age (FRA)?
Full Retirement Age (FRA) is the age at which you can begin collecting your Social Security retirement benefits without facing any reduction. For most people, reaching FRA means you’ll receive 100% of the benefits you’re entitled to based on your lifetime earnings record.
In the past, 65 was the standard age for FRA, but due to increasing life expectancies and the need to ensure Social Security’s long-term sustainability, the age has been gradually rising. As of 2025, 67 is the new FRA for individuals born in 1960 or later.
Is 65 or 67 Your Full Retirement Age: Full Retirement Age Timeline
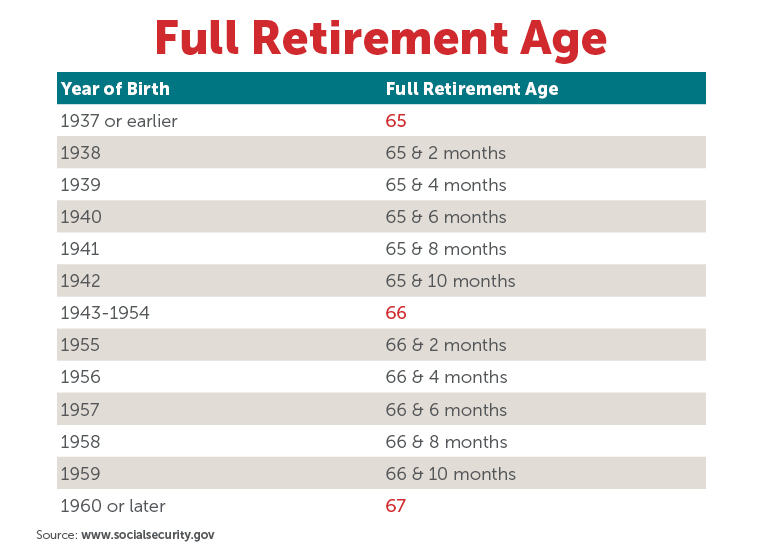
The Social Security Administration (SSA) made changes to FRA beginning in 1983, gradually increasing the age for those born after 1937. Here’s how the FRA breaks down for different birth years:
| Year of Birth | Full Retirement Age |
|---|---|
| 1943 – 1954 | 66 years old |
| 1955 | 66 years, 2 months |
| 1956 | 66 years, 4 months |
| 1957 | 66 years, 6 months |
| 1958 | 66 years, 8 months |
| 1959 | 66 years, 10 months |
| 1960 or later | 67 years old |
As you can see, those born 1960 and after will have to wait until 67 to claim full Social Security benefits.
How Does Your Full Retirement Age Affect Social Security Benefits?
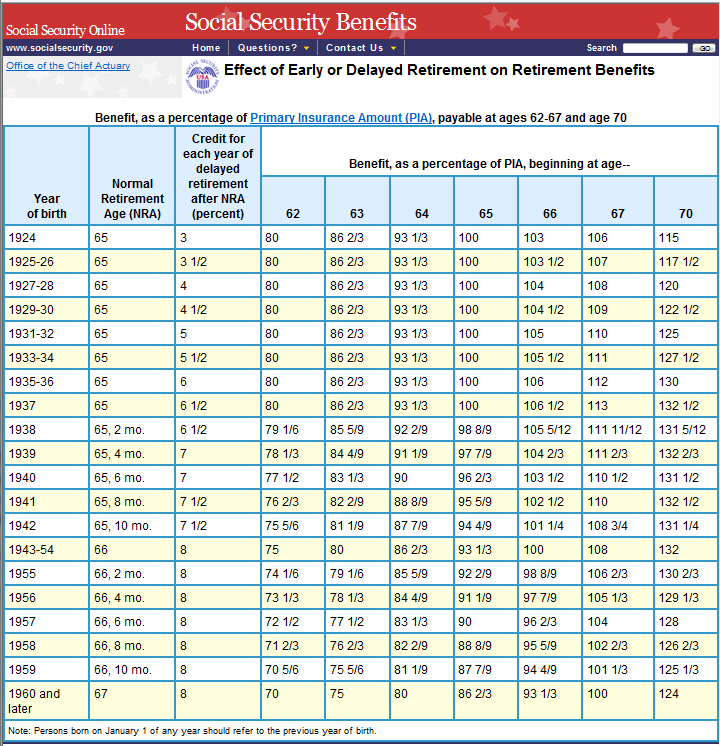
Your FRA determines when you can claim your full Social Security benefits. If you choose to claim your benefits before reaching FRA, the amount you’ll receive each month will be permanently reduced. The earlier you start, the smaller your monthly check will be.
For instance, if your FRA is 67 and you choose to start claiming at 62, your monthly benefit will be reduced by about 30%. While it might be tempting to start taking Social Security early, it’s essential to understand that this reduction lasts forever, so you’ll be receiving less money every month for the rest of your life.
On the other hand, delaying your benefits until after your FRA can actually increase your monthly Social Security payments. For each year you delay starting your benefits after your FRA, your payment amount increases by 8%. If you wait until age 70, your benefits will increase by 24% compared to claiming at 67.
When Should You Start Taking Social Security?
Determining when to start receiving Social Security benefits is a highly personal decision. Below are some of the key factors that should guide your decision:
- Health: If you’re in good health and your family has a history of longevity, delaying your benefits until age 70 could increase the amount you receive each month. However, if health concerns are a factor, you might want to start claiming earlier.
- Financial Needs: If you need income right away, it might make sense to start claiming at 62. However, if you can afford to wait, delaying could maximize your benefits.
- Work Plans: If you plan to continue working while collecting Social Security, be aware that earnings limits may reduce your benefits if you claim before your FRA.
- Life Expectancy: If you’re not sure how long you’ll live, claiming early could help ensure you receive some benefits even if you don’t live as long as expected.
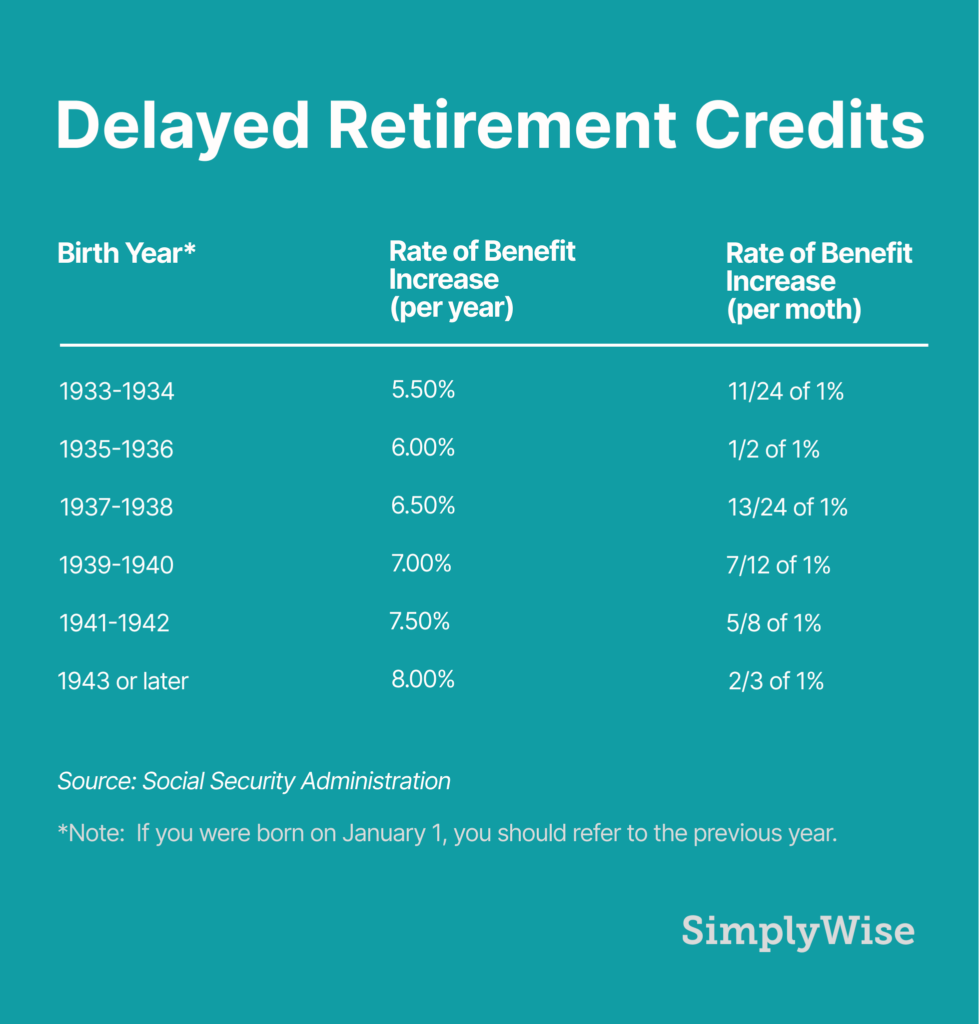
The Impact of Delayed Retirement
One of the most significant advantages of delaying Social Security benefits is the increase in monthly benefits. For each year you delay after reaching your FRA, your benefit increases by 8%, up to age 70.
Let’s break it down further:
Example 1: Claiming Social Security at 62 vs. 67 vs. 70
Assume your Primary Insurance Amount (PIA) at age 67 is $2,000 a month:
- If you claim at 62, you’ll receive only $1,400 a month (30% less).
- If you claim at 67 (your FRA), you’ll receive $2,000 a month.
- If you delay until 70, you’ll receive $2,480 a month (24% more than if you had claimed at 67).
Clearly, delaying your claim until age 70 can provide a significant boost to your monthly benefits.
Social Security Retirement Age Adjusted to 67 Under New Guidelines- Check Official Details!
U.S. Retirement Age Set to Rise Again as Social Security Faces Major Funding Crisis
Millennial Who Achieved Early Retirement Reveals Harsh Truth About FIRE Lifestyle







